Starter quiz
- Frequency density is proportional to the frequency per unit for the data in each class. Often, the multiplier is 1 meaning...
- Frequency density = frequency class width
- Frequency density = frequency class width ✓
- Frequency density = class width frequency
-
- Select which statements are true.
- Histograms can show discrete and continuous data. ✓
- Histograms show the distribution of data using grouped intervals. ✓
- Histograms with unequal bar widths must be plotted against frequency density. ✓
- Histograms with unequal bar widths must be plotted against frequency.
- Histograms with equal bar widths must not be plotted against frequency density.
-
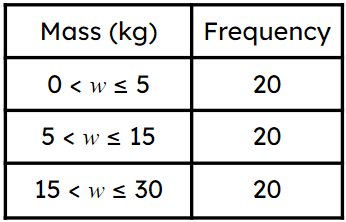 Here is some data on the masses of parcels. Which class interval shows a frequency density of 2?
Here is some data on the masses of parcels. Which class interval shows a frequency density of 2?-
- ✓
-
-
 Here is some data on the lengths of some string. Which class interval shows a frequency density of 1.4?
Here is some data on the lengths of some string. Which class interval shows a frequency density of 1.4?-
-
- ✓
-
-
 The histogram shows the masses of different parcels. How many parcels have a mass between 5 and 15 kg?
The histogram shows the masses of different parcels. How many parcels have a mass between 5 and 15 kg?- '20' ✓
- Select which of the following statements are true given a histogram with unequal bar widths plotted against frequency density.
- The highest bar shows the modal class.
- The bar with the largest area shows the modal class. ✓
- The frequency is the frequency density class width.
- The lowest bar shows the class width with the lowest frequency.
- The smallest bar area shows the smallest frequency. ✓
-
Exit quiz
- Which of the following shows the frequency in a histogram with unequal bar widths?
- The area of the bar ✓
- The height of the bar
- The length of the bar
- The frequency density
-
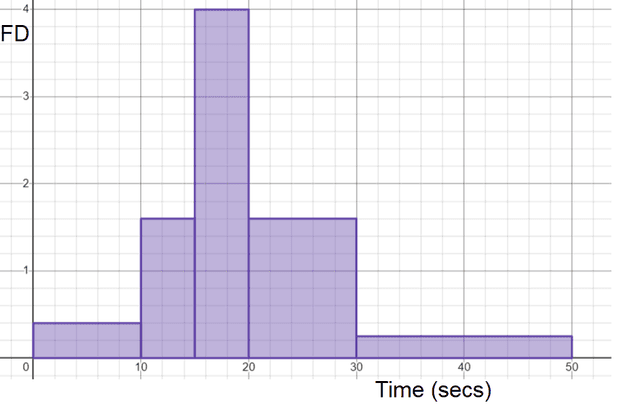 Here are the times taken to type the alphabet. Match the class intervals with the correct frequency density.
Here are the times taken to type the alphabet. Match the class intervals with the correct frequency density.- ⇔Frequency density = 0.4 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 1.6 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 4 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 0.25 ✓
 Here is some data on the lengths of some parcels. Match the frequency with the class interval.
Here is some data on the lengths of some parcels. Match the frequency with the class interval.- ⇔12 ✓
- ⇔15 ✓
- ⇔20 ✓
- ⇔4 ✓
 Here is a histogram showing lengths of different fruit. Which numbers represent , and on the axis?
Here is a histogram showing lengths of different fruit. Which numbers represent , and on the axis?- , and
- , and ✓
- , and
- and
-
 Here are the times taken to type the alphabet. Match the class interval to the correct frequency.
Here are the times taken to type the alphabet. Match the class interval to the correct frequency.- ⇔Frequency = 4 ✓
- ⇔Frequency = 8 ✓
- ⇔Frequency = 20 ✓
- ⇔Frequency = 16 ✓
- ⇔Frequency = 5 ✓
 Here is a histogram showing the time it takes to solve a puzzle.
Here is a histogram showing the time it takes to solve a puzzle.- ⇔Frequency = 10 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 6 ✓
- ⇔Frequency = 15 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 2.8 ✓
- ⇔Frequency density = 2.5 ✓
Worksheet
Presentation
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- A frequency table can be used to construct a histogram
- A histogram can be used to construct a frequency table
- Data is sometimes collected using uneven class widths
Common misconception
Histograms with unequal bar widths are plotted against the frequency and/or pupils read the frequency density as the frequency of the class width.
Show what a histogram with unequal bar widths looks like when plotted against frequency. This visual aid will show pupils the distribution of data is difficult to see.
Keywords
Continuous data - Continuous data can take any value within a range. (Height, mass, temperature)
Histogram - A histogram is a diagram consisting of rectangles whose area is proportional to the frequency in each class and whose width is equal to the class interval.
Frequency density - Frequency density is proportional to the frequency per unit for the data in each class. Often, the multiplier is 1 meaning that frequency density = frequency ÷ class width.